According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, by 2026, about 11.5 million jobs would be created for data science. In India, the data science role grew by 45% in 2021, with 93,500+ job openings all over the country. Furthermore, a recent study by Glassdoor states that a data scientist’s salary in India today is INR 12 Lakh per year.

How to Become a Data Scientist?
Get ready for a Journey that blends theory with real-life scenarios, making your initiation into the realm of data science a seamless and enjoyable experience.
Introduction
Welcome to the exciting world of data science! If you’re a newcomer eager to unravel the mysteries of data and transform it into meaningful insights, you’re in the right place. In this beginner’s guide, we’ll navigate through the vast landscape of data science, breaking down complex concepts into digestible bits. Get ready for a journey that blends theory with real-life scenarios, making your initiation into the realm of data science a seamless and enjoyable experience. At Analytics Jobs, you will gather all the essential information needed to choose the best course, institute and more.
Understanding the Basics
Imagine data as a treasure chest waiting to be opened. Data scientists are the modern-day treasure hunters, armed with analytical tools instead of maps. But before diving into the sea of data, let’s grasp the basics.
Data science is the art of extracting valuable insights from data. It involves collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data to guide decision-making.
In simple terms, data science is like being a detective for numbers. It’s about collecting, looking at, and understanding information (data) to solve real-world problems or make smart decisions. Data scientists use tools and skills to find patterns, trends, and useful insights hidden in the vast amount of data that is all around us. Imagine it as decoding the stories that numbers and facts tell, helping us understand things better and make informed choices.
Scenario : The Coffee Shop Conundrum
Imagine you run a coffee shop, and you notice sales fluctuating. A data scientist would collect data on various factors like weather, promotions, and customer footfall. By analyzing this data, patterns emerge, helping you understand the reasons behind the sales rollercoaster.
Data Science Job Roles
The field of data science offers a diverse range of job roles, each playing a unique part in extracting insights from data. Here are some key job roles in the data science domain:
|
S.no. |
Job Role |
Responsibility |
|
1. |
Data Scientist |
Analyzing and interpreting complex data sets, developing models and algorithms for prediction or classification, and providing actionable insights to solve business problems. |
|
2. |
Data Analyst |
Focusing on collecting, processing, and performing statistical analyses of data to uncover trends, patterns, and insights that can guide business decisions. |
|
3. |
Machine Learning Engineer |
Building and deploying machine learning models that enable systems to learn and make predictions or decisions without explicit programming. |
|
4. |
Data Engineer |
Designing, developing, and maintaining the architecture for data generation, transformation, and storage, ensuring a smooth flow of data for analysis. |
|
5. |
Business Intelligence (BI) Analyst |
Using tools to visualize data and create reports that help businesses make strategic decisions, often focusing on key performance indicators (KPIs). |
|
6. |
Statistician |
Applying statistical techniques to analyze and interpret data, providing valuable insights and aiding in decision-making processes. |
|
7. |
Quantitative Analyst |
Employing mathematical models and statistical techniques to analyze financial data, often working in finance to inform investment decisions. |
|
8. |
Data Architect |
Designing and creating the structure for databases and large-scale processing systems, ensuring data is stored and accessed efficiently. |
|
9. |
Data Science Manager/Director |
Overseeing the data science team, guiding projects, and aligning data science efforts with business goals. |
|
10. |
Big Data Engineer |
Managing and processing large datasets using tools like Hadoop and Spark, optimizing systems for efficient data storage and retrieval. |
|
11. |
IoT (Internet of Things) Data Scientist |
Analyzing data generated by IoT devices, extracting meaningful insights to improve efficiency, performance, and decision-making in various industries. |
|
12. |
AI (Artificial Intelligence) Research Scientist |
Conducting research to develop new algorithms and techniques, pushing the boundaries of AI capabilities. |
What is the Work of a Data Scientist?
A data scientist is like a detective who solves puzzles using information (data) instead of clues. Their job is to find valuable insights and patterns hidden in a sea of numbers and facts.
Scenario 1: The Retail Detective
Imagine you have a friend who owns a store. They notice that some products sell better at certain times. A data scientist would collect information about what people buy, when they buy it, and even factors like the weather. By analyzing this data, the data scientist can help your friend stock the right products at the right time, increasing sales.
Scenario 2: The Gaming Guru
Let’s say you’re into gaming. A data scientist in a gaming company might look at how players behave in a game. By studying this data, they can figure out what makes the game more fun or what might make players stop playing. It’s like having a friend who knows exactly what you want in a game before you even ask.
Key Tasks of a Data Scientist:
- Collecting Data: Imagine you’re baking cookies, and each ingredient is like a piece of data. The data scientist gathers these ingredients (data) to use later.
- Cleaning Data: Picture preparing the ingredients for baking by removing any bad ones. Data scientists clean up the data, getting rid of mistakes or things that don’t fit.
- Analyzing Data: Think of mixing ingredients to create the perfect cookie dough. Data scientists use tools to mix and analyze data, finding patterns that can help solve problems.
- Creating Models: Just as a recipe guides you in making cookies, data scientists create models (like instructions) that predict future outcomes based on past data.
Scenario 3: The Health Hero
Suppose you have a relative with a health condition. A data scientist in healthcare might use information from patient records to predict potential health issues. It’s like having a guardian angel who warns about possible problems before they happen.
Scenario 4: The Movie Matchmaker
Think about the last movie you loved. A data scientist at a streaming service analyzes what movies people watch. By understanding your preferences, they recommend movies you’re likely to enjoy. It’s like having a friend who always suggests the perfect film for you.
Making the World Smarter:
Data scientists use their skills to make things better and smarter. Whether it’s improving businesses, predicting health issues, or making entertainment more enjoyable, they’re like wizards turning raw data into magical insights.
So, in a nutshell, a data scientist is someone who explores data to uncover secrets, solve problems, and make the world a bit smarter and more efficient.
A Journey through the History of Data Science
Data science has its roots in the 1950s when statisticians and mathematicians began analyzing large datasets. The rise of computing power in the 1970s and 1980s led to the emergence of data science, integrating statistics, computer science, and domain knowledge.
The digital revolution in the 1990s and early 2000s saw the rise of big data, leading to the need for more sophisticated tools to extract meaningful insights. The mid-2000s saw the rise of open-source tools like R and Python, providing accessible platforms for data analysis.
The role of data scientists emerged in the late 2000s and early 2010s, requiring a blend of statistical expertise, programming skills, and domain knowledge. The 2010s saw the Big Data buzzword, reflecting the challenges and opportunities presented by vast datasets. Data science has become an integral part of various industries, with a focus on ethical considerations, privacy, and interpretability of models.
The journey of data science continues with ongoing advancements in technology, methodologies, and applications. Data scientists have transformed from mere analysts to influential decision-makers, revealing hidden patterns and predicting future trends.
Essential Skills for a Data Scientist
Becoming a proficient data scientist involves mastering a variety of skills that span technical, analytical, and domain-specific areas. Here are some essential skills for a data scientist:
- Statistical Knowledge:
Understanding statistical concepts is fundamental for interpreting and analyzing data accurately. Concepts such as probability, hypothesis testing, and regression analysis are essential tools for a data scientist.
- Programming Skills:
Proficiency in programming languages like Python or R is crucial for data manipulation, analysis, and building machine learning models. These languages provide the flexibility and libraries needed in the data science toolkit.
- Data Wrangling and Cleaning:
Dealing with messy and unstructured data is a common challenge. Data scientists must be skilled in cleaning and organizing data, handling missing values, and ensuring the dataset is ready for analysis.
- Data Visualization:
Communicating insights effectively is vital. Data scientists should be adept at creating meaningful visualizations using tools like Matplotlib, Seaborn, or Tableau to convey complex information in a clear and understandable manner.
- Machine Learning:
Understanding machine learning algorithms and when to apply them is key. Data scientists should be familiar with both supervised (e.g., classification, regression) and unsupervised (e.g., clustering) learning techniques.
- Deep Learning:
In the era of complex neural networks, having knowledge of deep learning frameworks like TensorFlow or PyTorch is beneficial. This skill is particularly relevant for tasks such as image recognition and natural language processing.
- Domain Knowledge:
Context matters. Having a solid understanding of the industry or domain in which the data is being analyzed allows data scientists to ask relevant questions, design meaningful experiments, and derive actionable insights.
- Database Knowledge (SQL):
Proficiency in SQL is crucial for extracting, manipulating, and analyzing data stored in databases. Data scientists often need to interact with databases to access the information they require.
- Collaboration and Communication:
The ability to communicate findings to both technical and non-technical stakeholders is essential. Collaboration with teams, including business analysts and decision-makers, ensures that data-driven insights lead to informed decisions.
- Problem-Solving Skills:
Data scientists are problem solvers at their core. They need to approach challenges methodically, breaking down complex problems into manageable steps and applying the right tools and techniques.
- Ethics and Privacy Awareness:
With great data comes great responsibility. Data scientists should be aware of ethical considerations, ensuring that their work respects privacy, avoids bias, and adheres to ethical guidelines.

Step-by-step Guide to Become a Data Scientist
Becoming a data scientist requires a combination of education, skills development, and practical experience. Here are the key requirements to embark on a successful journey toward becoming a data scientist:
1. Educational Background:
- Bachelor’s Degree: Typically in a quantitative field such as Computer Science, Statistics, Mathematics, Physics, or Engineering. Some data scientists also come from backgrounds in Economics or other sciences.
- Advanced Degree (Preferred): Many data scientists hold a Master’s or Ph.D. in a related field, providing a deeper understanding of statistical and machine learning concepts.
2. Programming Proficiency:
- Python and/or R: Mastery of at least one programming language is essential. Python is widely used in the data science community due to its versatility and extensive libraries. R is also popular, especially in academia.
3. Statistical Knowledge:
- A solid understanding of statistical concepts is crucial for data analysis. Topics like probability, hypothesis testing, and regression analysis form the foundation of statistical knowledge for a data scientist.
4. Data Wrangling and Cleaning:
- Proficiency in tools and libraries for data manipulation and cleaning, such as Pandas (Python) or Tidyverse (R).
5. Data Visualization:
- Ability to create meaningful visualizations using tools like Matplotlib, Seaborn (Python) or ggplot2 (R). Visualization skills help in communicating insights effectively.
6. Machine Learning Expertise:
- Understanding machine learning algorithms and when to apply them. Familiarity with popular machine learning libraries like Scikit-learn (Python) is essential.
7. Database and SQL Skills:
- Knowledge of working with databases and the ability to write SQL queries for data extraction and manipulation.
8. Big Data Technologies:
- Familiarity with big data tools like Hadoop and Spark, especially for handling large datasets.
9. Cloud Platforms:
- Experience with cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud, as many organizations store and process data in the cloud.
- Proficiency in using version control systems like Git for tracking changes in code and collaborating with others.
10. Problem-Solving Skills:
- Data scientists are problem solvers. The ability to break down complex problems, formulate hypotheses, and devise solutions is crucial.
11. Communication Skills:
- The capacity to communicate complex findings to both technical and non-technical stakeholders is essential. Clear communication ensures that data-driven insights are effectively utilized for decision-making.
12. Portfolio and Practical Projects:
- Building a portfolio showcasing real-world projects demonstrates practical skills and can be invaluable when applying for data science positions.
13. Networking:
- Engaging with the data science community through platforms like LinkedIn, attending conferences, and participating in meetups can provide valuable insights, mentorship, and career opportunities.
Data Scientist Job Outlook
Data science has experienced significant growth in recent years due to the increasing importance of data in making informed decisions across various industries. The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) in various sectors has fueled the need for skilled data scientists.
The proliferation of big data has created both challenges and opportunities for data scientists. Industry diversification has led to a demand for professionals with data science expertise in sectors like healthcare, finance, e-commerce, and manufacturing.
Technological advancements have also contributed to the evolution of the data science field, with organizations seeking skilled data scientists to stay at the forefront of innovation. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated digital transformation initiatives, making data-driven decision-making even more critical.
A global skills shortage is also a concern, but diverse job opportunities in various domains like healthcare informatics, finance, and cybersecurity are available. Remote work trends have opened up global job opportunities for data scientists, providing flexibility for both employers and job seekers.
Get Advice
Get Free Career
Counselling from
Experts
Book a Session with an Industry Professional today!
By continuing you agree to our Terms of Service and Privacy Policy, and you consent to receive offers and opportunities from the Analytics Jobs platform listed EdTech’s by telephone, text message, and email.
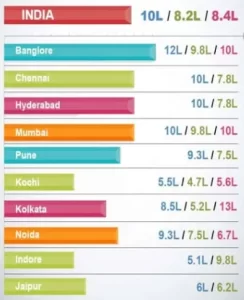
Salary of a Data Scientist
- Data Scientist Salary India
According to Glassdoor, the average salary for a data scientist in India is ₹14,00,000. The average supplemental cash compensation for a data scientist in India is from ₹82,250 to ₹3,10,000.
According to AmbitionBox, the salary range for a data scientist in India is ₹ 3.9 Lakhs to ₹ 27.9 Lakhs, with an average of ₹ 14.6 Lakhs per year.
- Data Science Salary Abroad

Conclusion
As you conclude this beginner’s guide, remember that the journey into data science is an ongoing adventure. Embrace challenges, stay curious, and keep honing your skills. You are now equipped with the knowledge to decipher the data mysteries and contribute meaningfully to the ever-evolving field of data science. Welcome aboard, aspiring data scientist – your journey has just begun!
Books and Online Resources
Books:
- “Python for Data Analysis” by Wes McKinney:
- An excellent resource for learning data manipulation and analysis with Python using Pandas and other key libraries.
- “The Elements of Statistical Learning” by Trevor Hastie, Robert Tibshirani, and Jerome Friedman:
- Provides a deep dive into statistical learning methods, essential for understanding the foundations of machine learning.
- “Hands-On Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn, Keras, and TensorFlow” by Aurélien Géron:
- A practical guide covering machine learning techniques with a hands-on approach using popular Python libraries.
- “Data Science for Business” by Foster Provost and Tom Fawcett:
- Focuses on the business side of data science, explaining how data-driven decisions impact various industries.
- “The Art of Data Science” by Roger D. Peng and Elizabeth Matsui:
- Offers insights into the practical aspects of data science through case studies and interviews with experienced practitioners.
- “Storytelling with Data” by Cole Nussbaumer Knaflic:
- Teaches the art of creating compelling visualizations to effectively communicate data-driven insights.
- “Deep Learning” by Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio, and Aaron Courville:
- A comprehensive guide to understanding deep learning, covering both theoretical concepts and practical applications.
- “Data Science from Scratch” by Joel Grus:
- Ideal for beginners, this book introduces key concepts and tools in data science using Python.
- “Applied Machine Learning” by Kelleher, Mac Namee, and D’Arcy:
- Focuses on practical applications of machine learning with real-world examples and case studies.
- “Python Machine Learning” by Sebastian Raschka and Vahid Mirjalili:
- A hands-on guide that covers machine learning concepts and algorithms using Python’s Scikit-learn and TensorFlow.
Online Resources:
- Coursera:
- Offers a variety of data science courses from top universities and organizations.
- edX:
- Similar to Coursera, edX provides online courses from universities around the world.
- Kaggle:
- A platform for data science competitions and collaborative learning. Kaggle also offers datasets and kernels for hands-on practice.
- DataCamp:
- Provides online courses and interactive coding challenges in data science, statistics, and machine learning.
- Towards Data Science on Medium:
- A popular publication with a wide range of articles covering topics in data science, machine learning, and artificial intelligence.
- GitHub:
- Explore data science projects and repositories on GitHub to learn from real-world examples and collaborate with others.
- UCI Machine Learning Repository:
- A collection of datasets for machine learning research and experimentation.
- Google AI:
- Google’s AI blog offers insights into the latest research and developments in artificial intelligence.
- YouTube Channels:
- Check out channels like Data School, Sentdex, and StatQuest for video tutorials on various data science topics.
- Stack Overflow:
- A community where you can ask questions, seek advice, and learn from experienced data scientists.
Frequent Asked Questions (FAQs)
Data Science is the field that involves extracting insights and knowledge from data through various techniques and methods. It is important because it helps businesses make informed decisions, discover patterns, and gain valuable insights, leading to improved efficiency and strategic planning.
While a specific educational background in fields like Computer Science, Statistics, or Mathematics is beneficial, it’s not mandatory. Many successful data scientists come from diverse academic backgrounds. What matters most is a strong foundation in analytical thinking and problem-solving.
Python and R are widely used in data science. Python, with its versatility and extensive libraries, is particularly popular. Learning either language, or both, will equip you with the necessary tools for data manipulation, analysis, and machine learning.
While advanced degrees can enhance your profile, they are not strictly necessary. Many data scientists enter the field with a bachelor’s degree. What’s crucial is a solid understanding of data science concepts, strong skills, and the ability to apply them effectively.
Key skills include programming, statistical knowledge, machine learning, data wrangling, data visualization, and domain expertise. Effective communication and problem-solving skills are also critical for success in the field.
Building a portfolio of hands-on projects is crucial. Work on real-world problems, participate in data science competitions (such as those on Kaggle), and contribute to open-source projects. Practical experience showcases your skills to potential employers.
Some recommended resources include online platforms like Coursera and edX, books like “Python for Data Analysis” by Wes McKinney, and interactive learning platforms like DataCamp. Continuous learning from a variety of sources is key.
Certifications from reputable organizations like Coursera, edX, or Microsoft can boost your profile. However, they are supplementary, and hands-on experience and practical skills often carry more weight in the industry.
Domain knowledge is valuable but not always mandatory. Having a good understanding of the industry you’re working in enhances your ability to ask relevant questions and derive meaningful insights. However, it can be acquired on the job.
Data visualization is crucial for communicating insights effectively. Tools like Matplotlib, Seaborn, or Tableau help in presenting complex findings in a clear and understandable manner, making data more accessible to stakeholders.
Recent Posts
- IIT DELHI LAUNCHES CERTIFICATE PROGRAM TO HELP STUDENTS IN ENGINEERING. 26-07-2024
- MedLearn OPENS A NEW CAMPUS IN BENGALURU TO HELP HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONALS. 26-07-2024
- BYJU’S INSOLVENCY: BYJU RAVEENDRAN FILES NEW APPEAL AGAINST NCLT ORDER IN KARNATAKA HIGH COURT. 26-07-2024
- ApplyBoard AND TD ANNOUNCE A NEW COLLABORATION TO EMPOWER INDIAN STUDENTS. 24-07-2024
- StudyMEDIC AND OC Academy PROVIDE CLINICAL FELLOWSHIP PROGRAMS FOR MEDICAL CANDIDATES. 23-07-2024
