The transportation url is actually starting to use Artificial Intelligence (AI) in mission critical tasks (for instance, self driving automobiles carrying passengers) in which the reliability as well as security of an AI system will be below question coming from the common public. Major issues of the transportation market as capability troubles, environmental pollution, reliability, safety, and wasted energy are actually providing ample opportunity (and potential for higher ROI) for AI innovation.
For the benefit of this post,’ transportation’ is going to include all systems which move luggage as well as folks. Of the course of this document we wish to reply to the following questions:
- What AI technologies are presently used in conveyance apps? What’s active in the procedure of AI integration for these apps?
- What exactly are the present use cases man-made intelligence transportation?
- So what can we expect in phrases of the technology roadmap going ahead?
Depending on the apps discovered in the analysis of ours, we segment AI in the transportation market as follows:
- Current applications
- Public passenger transportation
- Autonomous trucks
- AI applications in railway cargo transportation
- Just around the corner
- Transportation planning
- Future applications
We explore each of the applications and the future of their technology roadmap in more detail below.
Current Applications
The compatibility of AI to transportation apps is actually a relatively natural match. Nevertheless, as well as the situation with AI in a number of other industries, the adoption of these apps currently differs across geographies as well as industries.
That properly translates to the point that AI application in transport could paradoxically be equally straightforward and complicated, probable and implausible, just-around-the-corner and distant, based on environment as well as geographical elements. We check out a couple of cases for present programs of AI in the transportation industry below:
1 – Public Passenger Transportation
Autonomous Buses
Small scale autonomous bus trials have been initiated around the globe in the latest times most prominently in Finland, Singapore and China. The worldwide non uniformity within built up buildings, city infrastructures, street surfaces, weather patterns, traffic patterns etc. make AI uses in autonomous trucks for on time delivery of packages as well as individuals, highly environment unique.
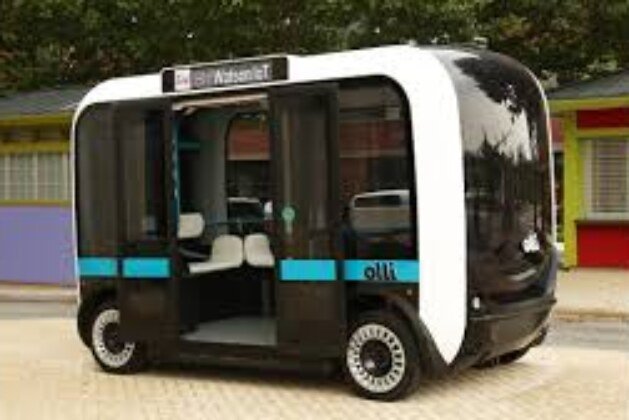
Olli by Local Motors
Olli is a self driving ,’ cognitive’ electrical shuttle out of American company Local Motors. The business is centered on volume manufacturing that is lower of open source automobile models, utilizing several microfactories.
Driven by IBM’s Watson Internet of Things (IoT) for Automotive, Olli is able to carry out features as transportation of passengers to requested locations, supplying ideas on regional sights as well as answering questions regarding how Olli’s self driving service functions. According to IBM, 5 developer APIs from the Watson IoT for Automotive platform was incorporated with Olli like Speech to Text, Natural Language Classifier, Conversation, Entity Extraction and Text to Speech.
Traffic Management Operations
AI answers have been often used in handling management as well as seo issues. Company executives will discover it fascinating to remember that AI is already being used in uses as detection and prediction of traffic accidents as well as problems (by transforming traffic sensors into’ intelligent’ agents with cameras). We talk about the situation of Rapid Flow Technologies, a Carnegie Mellon Faculty spin off.
Surtrac by Rapid Flow Technologies
Headquartered in Pittsburg, Rapid Flow technologies’ Surtrac system was originally developed in the Intelligent Coordination and Logistics Laboratory in the Robotics Institute at Carnegie Mellon University as part of the Traffic21 research initiative. Rapid Flow is also a part of the NSF I-Corps Site program at Carnegie Mellon.
In June 2012, Rapid Flow installed the Surtrac system for a pilot in the East Liberty neighborhood of Pittsburgh. The solution was a network of nine traffic signals in three major roads (Penn Circle, Penn Avenue, and Highland Avenue). Rapid Flow claims that Surtrac helped reduce travel times by more than 25% on average, and wait times declined an average of 40% during the course of the trial. Following the pilot project, Rapid flow has collaborated with local Pittsburg administration to expand the solution to other parts of the city (around 50 traffic signals). Readers may also see our previous post on artificial intelligence application in smart cities for more on Surtrac.
2 – Autonomous Trucks
The transportation business is actually confronting environmental difficulties as well as stricter emission regulations from government agencies. A report by the International Transport Forum (ITF)claims that autonomous trucks will save costs, lower emissions, and boost road safety as in comparison to conventional trucking with human motorists. We talk about the present main use cases for autonomous trucks here:
Uber Advanced Technologies Group
In October 2016, San Francisco startup Otto (now called Uber Advanced Technologies Group after being bought by Uber for $680 million in 2017) successfully completed the world’s first autonomous truck delivery carrying around 50,000 cans of Budweiser beer over a distance of 120 miles from Fort Collins to Colorado Springs, CO.
According to Uber ATG, the uniform patterns in highway driving and the fact that highways form only 5% of the roads in the US make it an ideal application for self-driving. Although at the time of this writing, a crash during testing has forced the company to suspend autonomous tests in Arizona and pause its Pittsburgh operations.
TuSimple
TuSimple a Chinese startup, founded in 2015, successfully completed a 200-mile level 4 (see the standard levels of autonomous driving) test drive for a driverless truck passed from Yuma, Arizona, to San Diego, California. TuSimple claims that it’s driving system was trained using deep learning to simulate tens of millions of miles of road driving.
TuSimple uses Nvidia graphic processing units (GPUs) including the NVIDIA DRIVE PX 2 computer, TensorRT deep learning inference optimizer and runtime engine, Jetson TX2 AI supercomputer on a module, CUDA parallel computing platform and programming model, and cuDNN CUDA deep neural network library. At the time of writing there was no information available on the specifics of the integration.
3 – AI Applications in Railway Cargo Transportation
GE Transportation
GE transportation has made a serious effort towards implementing artificial intelligence of the transportation url. The company has developed’ intelligent’ locomotives to enhance the effectiveness (which translates to economic benefit) of the rail transport strategies of theirs.
Each of GE’s sensible freight locomotives is equipped with sensors including cameras which shoot the, back, front, and track cab of the locomotive. The information from the sensors is actually given to machine-learned analytic uses which aggregate the information right there on the edge gateway, enabling onboard real time decision making.
Based on this article, the CTO of GE transportation, Wesley Mukai states, in phrases of outcomes GE saw gains in precision as well as quickness of detecting things on or perhaps near the track. Additionally, throughout the pilot project with Deutsche Bahn in Germany, a twenty five % reduction in locomotive failure rates was captured. Though, it’s not clear what the baseline readings for these metrics were, therefore a concrete measurable effect might not be doable at the time of writing.
Hitachi
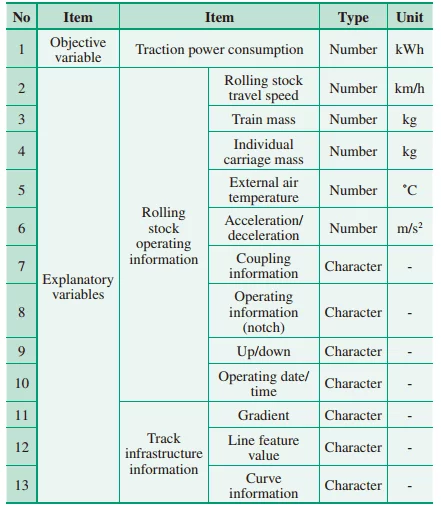
Hitachi has initiated a pilot project using its in house AI technology to lessen power consumed within traveling rolling stock. The AI platform is actually given inputs from 9 parameters of rolling stock operational details, like carriage speed, and 3 parameters applicable to monitor infrastructure, like the gradient. (See figure below)
The proper mixture of the elements for optimum energy efficiency is actually extracted by the platform. A comprehensive summary of the objective variable as well as outside parameters used to draw out optimum traction power is actually provided below. Hitachi promises that they’ve witnessed annual traction power usage decreasing by about twenty % as when compared with conventional operations. Though no additional information about the time frames of the project were readily available.
Just Around the Corner
According to the Stanford’s Artificial Intelligence and Life in 2030 – One Hundred Year Study, in the near future, AI is apt to get an increasingly extreme effect on community infrastructure by providing correct predictive behavioral versions of individuals’ moves, the preferences of theirs, and the objectives of theirs.
The United States Department of Transportation released a call for proposals (USDoT) in 2016 asking medium size cities to picture sensible city infrastructure for conveyance. USDoT plans to award forty million dollars to one city for demonstrating just how information and technology could be utilized to reimagine the motion of individuals in addition to goods.
According to the US transportation research board, emerging uses of AI in transportation planning are actually in traveling behavioral versions, community infrastructure design and preparing, and need modeling for public and luggage transport.
One restraint for the adoption of AI in transportation planning apps is the fact that attached conveyance infrastructure will even raise concerns about the privacy of individuals as well as the safety of private data. Government as well as legal laws about these honest considerations are going to dictate the pace of adoption and innovation for the market of the direct period.
A Gist of Future Use-Cases
Compiled below is a summary of primary features of artificial intelligence of conveyance apps which are presently starting to be commercialized or perhaps under investigation trials.
| S.No | AI Function | Typical use-case |
| 1 | Nonlinear prediction (Prediction of the behavior of systems in which inputs and outputs are non-linear) | Traffic demand modeling, or in modeling the transportation infrastructure health as a function of traffic, construction and weathering. |
| 2 | Control Functions | Signal control of traffic at road intersections, ramp metering on freeways, dynamic route guidance, positive train control on railroads |
| 3 | Pattern recognition | Automatic incident detection, image processing for traffic data collection and for identifying cracks in pavements or bridge structures and transportation equipment diagnosis. |
| 4 | Clustering | Identifying specific classes of drivers based on driver behavior, for example. |
| 5 | Planning | AI-based decision support systems for transportation planning as discussed in the sections below. |
| 6 | Decision making | Deciding whether to build a new road, how much money should be allocated to maintenance and rehabilitation activities and which road segments or bridges to maintain, and whether to divert traffic to an alternative route in an incident situation. |
| 7 | Optimization | Designing an optimal transit network for a given community, developing an optimal work plan for maintaining and rehabilitating a pavement network, and developing an optimal timing plan for a group of traffic signals. |
Source: Transportation Research Board (division of the National Research Council of the United States )
Concluding Thoughts – Impact of AI on Jobs in the Transportation Industry
A report by the International Institute for Sustainable Development testing of fully autonomous long-distance trains are already underway.
Another report published by the “Artificial Intelligence, Automation, and the Economy,” Executive Office of the U.S. President in 2016 states that 2.2 to 3.1 million truck train or taxi driver jobs could be impacted by self-driving vehicle technology in the United States. The report also states that on-demand car services, like Uber, will make a complete transition to autonomous operations in the near future.
While AI will influence a major amount of blue collar jobs in the transportation business, the different degrees of adoption throughout geographies as well as the but unfulfilled requirement of establishing honest laws are several restraints which could make change a slower procedure.
Readers with a strong interest interest in the economic impact of AI might enjoy the following interviews on our AI podcast:
- Technological Unemployment and the Role of Man and Machine – with Marshall Brain
- Surviving the Machine Age – Understanding the Trends Behind Technological Job Loss– with Professor Kevin La Grandeur
- Rise of Workforce Automation, “Blue Collar” and “White Collar” – with Martin Ford
Source: Raghav Bharadwaj from emerj.com