Introduction
What is Product Management and What is the Work of a Product Manager?
Imagine you’re the captain of a ship, navigating through uncharted waters, with the destination being a product that users will love. That’s the essence of being a Product Manager (PM). A PM wears many hats – part visionary, part diplomat, and always a problem-solver. You’re the heartbeat of the product, ensuring it evolves with the ever-changing demands of users and the market.
Scenario 1: Meet Alex, an imaginary PM in a tech company.
Picture this: Alex, armed with a whiteboard marker, sketching out the next big feature while juggling feedback from developers, designers, and the sales team. It’s a symphony of ideas, and Alex is the conductor.
In simple terms, imagine you have a cool idea for a game or an app. A product manager’s job is to make that idea a reality. They work with different teams, like designers and developers, to make sure everything runs smoothly. It’s like being the glue that holds everyone together, making sure the product is awesome and loved by people. In simple terms, a product manager turns ideas into real, amazing things!
Product Management Career Path
Product management offers a plethora of career paths, each catering to unique skills and interests. Aspiring professionals in this field can choose from various roles that align with their strengths and career objectives. Here are some prominent types of careers in product management:
- Product Manager:
The quintessential role, a Product Manager oversees the entire product development lifecycle. They are responsible for defining the product strategy, coordinating cross-functional teams, and ensuring the successful launch and growth of the product in the market.
- Technical Product Manager:
This role requires a deep understanding of technology and the ability to bridge the gap between technical and non-technical teams. Technical Product Managers work closely with development teams, translating business requirements into technical specifications.
- Product Owner:
In agile environments, the Product Owner collaborates with development teams to prioritize and manage the product backlog. They play a pivotal role in ensuring that the product features align with the overall business strategy.
- UX/UI Product Manager:
Focused on user experience (UX) and user interface (UI) design, professionals in this role concentrate on creating products that are not only functional but also provide an optimal user experience. They collaborate with designers and developers to bring user-centric designs to life.
- Data Product Manager:
With the increasing reliance on data-driven decision-making, Data Product Managers specialize in products that involve data analytics and insights. They work with data scientists and analysts to develop products that leverage data to meet business objectives.
- E-commerce Product Manager:
Specializing in the realm of online retail, E-commerce Product Managers focus on creating and enhancing digital products that facilitate online transactions. They need a deep understanding of consumer behavior and market trends in the e-commerce space.
- Platform Product Manager:
Platform Product Managers work on products that serve as a foundation for other applications or services. They ensure the platform meets the needs of various stakeholders and supports the development of complementary products.
- Digital Product Manager:
In an era dominated by digital transformation, Digital Product Managers focus on products in the digital realm, such as mobile apps, websites, or digital services. They need to stay abreast of technological trends and user expectations in the digital space.
- Product Marketing Manager:
Product Marketing Managers concentrate on promoting and positioning products in the market. They collaborate with product managers to understand product features and benefits, creating compelling marketing strategies to drive product adoption.
- Innovation Manager:
Innovation Managers are tasked with fostering creativity and driving innovation within an organization. They explore new ideas, technologies, and approaches to keep the product portfolio ahead of the curve.
- Start-up Product Manager:
Working in a start-up environment requires adaptability and a hands-on approach. Start-up Product Managers are often involved in various aspects of product development, from strategy to execution, in dynamic and fast-paced settings.
What is the Work of a Product Manager?
Product Strategy and Vision:
- Define Product Vision: Develop a clear and inspiring vision for the product, aligning it with the company’s overall goals.
- Create Product Strategy: Formulate a strategic plan outlining how the product will achieve its long-term objectives.
Market Analysis and Research:
- Market Understanding: Stay informed about market trends, competitor products, and customer needs.
- User Research: Conduct thorough research to understand user preferences and expectations.
Roadmap Development:
- Product Roadmap: Develop and maintain a detailed product roadmap, outlining the timeline for feature releases and updates.
- Prioritization: Prioritize features and improvements based on user feedback, market trends, and business goals.
Cross-Functional Collaboration:
- Team Coordination: Work closely with cross-functional teams, including design, development, and marketing, to ensure alignment and effective collaboration.
- Communication Skills: Facilitate clear communication between teams, ensuring everyone is on the same page regarding project goals and timelines.
User Feedback and Iteration:
- Feedback Collection: Actively seek and collect user feedback through various channels.
- Iterative Improvement: Use user feedback to iterate on product features and enhance user experience continuously.
Product Launch and Marketing:
- Launch Strategy: Develop comprehensive launch plans for new product features or versions.
- Collaboration with Marketing: Coordinate with the marketing team to ensure effective promotion and communication of product launches.
A Journey Through the History of Product Management
Product management has evolved over time, starting in the early 20th century in the United States. It evolved into a key decision-maker responsible for understanding market needs, overseeing product development, and orchestrating successful launches.
The marketing era saw product managers aligning product features with consumer preferences, integrating market research and advertising. The rise of technology in the late 20th century necessitated a more technical understanding of products, leading to the multidisciplinary role we recognize today.
The 21st century saw the rise of agile methodology, fostering collaboration between cross-functional teams. Globalization and digital transformation further shaped the role, requiring product managers to navigate global markets, leverage data analytics, and stay updated with emerging technologies. Today, product management is a strategic function with strong leadership, communication, and problem-solving skills.
Essential Skills for a Product Manager
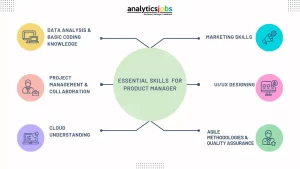
A Product Manager needs a blend of technical and non-technical skills to effectively navigate the complex landscape of product development. Here are some essential technical skills for a Product Manager:
Data Analysis:
- Understanding Metrics: The ability to interpret and draw insights from data analytics is crucial. Product Managers should be comfortable working with tools like Google Analytics, Mixpanel, or other data analysis platforms.
Basic Programming Knowledge:
- Coding Awareness: While not required to be a coding expert, having a basic understanding of programming languages (such as HTML, CSS, or Python) can facilitate effective communication with development teams.
UI/UX Understanding:
- Design Principles: A grasp of user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) principles helps in collaborating with design teams. Familiarity with design tools like Sketch or Figma is beneficial.
API Understanding:
- Integration Knowledge: Understanding how different software systems interact through APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) aids in planning and coordinating product features.
Database Fundamentals:
- Database Understanding: A basic knowledge of databases, SQL, and data structures helps in comprehending and communicating technical requirements to development teams.
Agile Methodology:
- Scrum and Kanban: Familiarity with Agile methodologies like Scrum and Kanban is crucial for efficient project management and collaboration with development teams.
Technical Documentation:
- Writing Technical Documents: The ability to create clear and concise technical documentation helps in communicating requirements, specifications, and project updates effectively.
Quality Assurance (QA) Understanding:
- Testing Concepts: A basic understanding of software testing and quality assurance processes aids in ensuring that the product meets the desired standards.
Project Management Tools:
- Tools Mastery: Proficiency in project management tools such as Jira, Trello, or Asana is essential for organizing tasks, tracking progress, and managing timelines.
Version Control Systems:
- Git Understanding: Knowledge of version control systems like Git helps Product Managers collaborate with development teams and manage code changes efficiently.
Market Research Tools:
- Competitor Analysis: Familiarity with tools for market research and competitor analysis, such as SEMrush or SimilarWeb, aids in making informed product decisions.
Understanding Cloud Technologies:
- Cloud Platforms: Awareness of cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud can be beneficial, especially when dealing with cloud-based solutions.

A Step-by-Step Guide on How to Become a Product Manager
Here’s a comprehensive step-by-step guide to become a product manager:
Step 1: Obtain the Right Educational Background
Begin by pursuing a Bachelor’s Degree in Business Administration. This foundation provides you with essential knowledge in business principles. To enhance your credentials further, consider pursuing a Master of Business Administration (MBA).
Step 2: Develop Leadership Skills
Cultivate strong communication and organizational skills, along with a heightened sense of emotional intelligence. These qualities are essential for effective leadership and collaboration with cross-functional teams.
Step 3: Gain Practical Experience
Actively seek opportunities to gain hands-on experience in roles that involve project management, team collaboration, and product development. Practical experience is invaluable for understanding the intricacies of the product management field.
Step 4: Acquire Product Management Certification
While not mandatory, obtaining a product management certification can significantly boost your credibility as a candidate. Look for reputable certification programs that align with industry standards.
Step 5: Hone Technical Skills
Familiarize yourself with product management tools and technologies. Develop proficiency in software used for user tracking, analysis, road mapping, and customer service. Technical expertise is a crucial aspect of the product manager’s role.
Step 6: Build a Strong Professional Network
Connect with professionals in the product management field through networking events, online platforms, and industry conferences. A robust professional network can provide valuable insights, mentorship, and potential job opportunities.
Step 7: Showcase Your Achievements
Create a compelling resume and online portfolio highlighting your education, skills, and practical experience. Clearly articulate how your background aligns with the requirements of a product manager role.
Step 8: Apply for Entry-Level Positions
Start applying for entry-level positions in product management or related fields. Look for opportunities to demonstrate your skills and willingness to learn. Many product managers begin their careers in associate or assistant roles.
Step 9: Seek Professional Growth
As you gain experience, aim for career advancement opportunities within your organization or explore leadership roles in larger companies. Continuously seek ways to enhance your skills and contribute to the success of the products you manage.
Product Manager Job Outlook
The employment landscape for Product Managers exhibits promising trends, with a positive outlook projected for the foreseeable future. Several factors contribute to this optimistic job market scenario:
- Growing Demand: The demand for skilled Product Managers continues to rise across various industries. Companies recognize the pivotal role these professionals play in steering product development, enhancing competitiveness, and meeting customer needs.
- Expanding Industries: As industries such as technology, healthcare, and e-commerce expand, the need for adept Product Managers grows proportionally. This expansion creates diverse opportunities for individuals aspiring to enter or advance within the field.
- Emphasis on Innovation: In today’s dynamic business environment, innovation is a driving force. Product Managers, being instrumental in the innovation process, are increasingly sought after to spearhead new product initiatives and improve existing offerings.
- Globalization: With businesses operating on a global scale, there is a heightened need for Product Managers who can navigate the complexities of international markets, understand diverse customer bases, and tailor products to meet varying needs.
- Technology Advancements: The continuous evolution of technology introduces new challenges and opportunities. Product Managers with a strong grasp of emerging technologies, data analytics, and digital trends are particularly in demand.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: The collaborative nature of product management, requiring effective communication and coordination across different departments, highlights the importance of skilled Product Managers in fostering cohesion within organizations.
- Remote Work Trends: The increasing acceptance of remote work provides flexibility for professionals in the field. This trend allows companies to access a broader talent pool and provides Product Managers with the opportunity to work for organizations regardless of geographical constraints.
Get Advice
Get Free Career
Counselling from
Experts
Book a Session with an Industry Professional today!
By continuing you agree to our Terms of Service and Privacy Policy, and you consent to receive offers and opportunities from the Analytics Jobs platform listed EdTech’s by telephone, text message, and email.
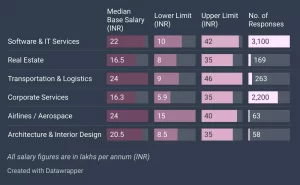
Salary of a Product Manager
- Product Manager Salary India
According to Glassdoor, The average income for a Product Manager in India is <30 Lakh per year, with a range of 1,00,000 – 3,87,500 in additional cash compensation.
According to AmbitionBox, product Manager salaries in India range from 5.4 Lakhs to 37.1 Lakhs per year, with an average yearly income of 21.3 Lakhs.
- Product Manager Salary Abroad
Product Manager Salary in Canada: $142,150. Product Manager Salary in Germany: €60,643. Product Manager Salary in France: €55,000. Product Manager Salary in Chicago: $117,450.
Conclusion
Becoming a successful product manager is a multifaceted journey that requires a combination of education, experience, and ongoing self-improvement. By honing analytical, communication, and strategic skills, aspiring product managers can navigate the complex landscape of product development and contribute significantly to their organization’s success.
Books and Online Resources
Books:
- “Inspired: How To Create Products Customers Love” by Marty Cagan
- This book provides valuable insights into the product management process, emphasizing the importance of creating products that resonate with customers.
- “Lean Product and Lean Analytics” by Ben Yoskovitz and Alistair Croll
- Offering a comprehensive guide to lean methodologies, these books explore ways to build successful products through iterative processes and data-driven decision-making.
- “Hooked: How to Build Habit-Forming Products” by Nir Eyal
- Nir Eyal delves into the psychology behind creating products that engage users and build lasting habits, a crucial aspect of successful product management.
- “Cracking the PM Interview: How to Land a Product Manager Job in Technology” by Gayle Laakmann McDowell and Jackie Bavaro
- Geared towards aspiring Product Managers, this book provides practical advice on navigating the product management interview process.
- “The Lean Startup: How Today’s Entrepreneurs Use Continuous Innovation to Create Radically Successful Businesses” by Eric Ries
- While not solely focused on product management, this book is essential for understanding lean startup principles and fostering an innovative mindset.
Online Resources:
- ProductCoalition.com
- An online community and publication platform that offers a wealth of articles, insights, and resources related to product management.
- MindTheProduct.com
- A hub for product management professionals, Mind the Product provides articles, webinars, and conferences to keep you updated on industry best practices.
- Udemy – “Become a Product Manager | Learn the Skills & Get the Job”
- This online course covers a wide range of product management skills, making it suitable for both beginners and those looking to enhance their expertise.
- PragmaticInstitute.com
- Pragmatic Institute offers training and resources for product managers, focusing on practical skills and strategies for success in the field.
- ProductPlan Blog
- ProductPlan’s blog features articles on various aspects of product management, providing practical tips and insights for both new and experienced professionals.
Frequent Asked Questions (FAQs)
Product Managers are responsible for the end-to-end development and success of a product. They oversee everything from conception to launch, ensuring that the product meets customer needs and aligns with business goals.
While there isn’t a strict requirement, a Bachelor’s Degree in Business Administration is often beneficial. Pursuing a Master’s in Business Administration (MBA) can enhance your qualifications and increase your chances of landing a product management role.
While prior experience in product management is advantageous, it’s not always mandatory. Entry-level positions and internships in related fields, combined with a strong educational foundation, can pave the way for a successful transition into product management.
Key skills include strong communication, leadership, analytical thinking, and a customer-centric mindset. Technical proficiency with product management tools and a knack for problem-solving are also highly valued.
Seek opportunities for internships, co-op programs, or entry-level positions in roles related to project management, product development, or business analysis. Hands-on experience is invaluable in understanding the intricacies of the field.
While not mandatory, obtaining a product management certification can enhance your credibility and make you a more competitive candidate. It demonstrates a commitment to the profession and a solid understanding of industry best practices.
Consider reading “Inspired: How To Create Products Customers Love” by Marty Cagan, “Lean Product and Lean Analytics” by Ben Yoskovitz and Alistair Croll, and “Cracking the PM Interview” by Gayle Laakmann McDowell and Jackie Bavaro.
Attend industry events, join online forums and communities, and connect with professionals on platforms like LinkedIn. Networking provides insights, mentorship, and potential job opportunities.
Platforms like Udemy offer courses such as “Become a Product Manager | Learn the Skills & Get the Job,” providing a structured curriculum for beginners and those looking to enhance their expertise.
The job outlook for Product Managers is optimistic, with growing demand across various industries. The role’s importance in driving innovation and meeting customer needs positions it as a key player in today’s dynamic business environment.
Recent Posts
- IIT DELHI LAUNCHES CERTIFICATE PROGRAM TO HELP STUDENTS IN ENGINEERING. 26-07-2024
- MedLearn OPENS A NEW CAMPUS IN BENGALURU TO HELP HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONALS. 26-07-2024
- BYJU’S INSOLVENCY: BYJU RAVEENDRAN FILES NEW APPEAL AGAINST NCLT ORDER IN KARNATAKA HIGH COURT. 26-07-2024
- ApplyBoard AND TD ANNOUNCE A NEW COLLABORATION TO EMPOWER INDIAN STUDENTS. 24-07-2024
- StudyMEDIC AND OC Academy PROVIDE CLINICAL FELLOWSHIP PROGRAMS FOR MEDICAL CANDIDATES. 23-07-2024

