In the modern era of digitalization, everyone is excited about emerging technologies that change the face of the modern lifestyle.
Over recent years, almost every enterprises ride the trend of digitalization and remain to adapt technologies like cloud computing and create their digital infrastructure the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) has increased in the cyber-security community as a staple in offering security to companies in a more and more complex threat landscape.
Artificial intelligence is used for automated, targeted hacking is set to be among the main threats to look out for in 2020. The tools and resources for developing malicious artificial intelligence and machine learning codes are the mainstream and there is a large amount of data for hackers to collect and use. We will encounter several AI tools for targeted and automated attacks.
The concept of a Computer Program Learning to attack by itself and expanding its knowledge base to be more advanced is SCARY. However, it’s a major concern, how the cyber-threat landscape has developed in recent years and is viewed as a main threat to the global economy.
Unfortunate as it may be, the AI technology has been exploited against enterprises often, with stats depicting a bleak picture, with more and more cyber-criminals powered by AI for launching more sophisticated cyber-attacks. One this kind of dark aspect of AI reveals itself in “Deepfakes.”
With Good comes Evil i.e. With the evolving technologies, drawbacks are evolving symantaneously. Deepfake is one of them.
What is Deepfake?
Deepfake is a term derived from ‘Deep Learning’ and ‘Fake’. It is a feature of AI-based technology used to create fake video and audio files that look and sound real.
In video altering, Deepfakes is the new technique. The technique creates a video of the user from a profile photo-based mostly on artificial intelligence (AI) and deep learning algorithms through the Python programming language. It is a risk in many aspects and based on Hany Farid, a Dartmouth researcher that specializes in media forensics to root away deepfakes, the technique “creates chances of false information, election tampering, and fraud.”
Deepfake media can be created by anyone with just a computer and an internet connection. This is accomplished by using a machine learning system known as Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN). It flags the bugs in the forgery until they start to be undetectable. The whole process of development may be automated at scale without busting a sweat.
History of Deepfake
Although academic interest associated with deepfakes dates back to 1997, deepfake came into the public domain in 2017. It began with a group of Reddit users that implemented AI to swap faces of celebrities with some other movie characters.
Stealing credit card information, talking down sites, or Defacing was regarded as major instances of cyberattacks. However, these attacks were costly since they demanded attackers to devote resources and more time. With AI, an attacker is able to carry out repeated and multiple strikes on the network of any organization by programming a few lines of code to do the majority of the work.
Can Deepfake Technology help in enhancing the Future
Recent advances in deepfake video technology have resulted in the rapid increase of such videos in the public domain in the past few years. Face-swapping apps like Zao, for instance, permit users to swap their faces with a celebrity, creating deepfake videos easily.
These advancements are the result of Deep Generative Modeling, a new technology that enables us to generate duplicates of real faces and build new, and impressively real-life pictures, of users who do not exist.
This new technology has rather raised concerns about identity and privacy. If our faces can be replicated by an algorithm, would it be feasible to replicate more details of our personal digital identity or attributes like the voice – or produce a true body double?
In fact, technology has progressed rapidly from duplicating simply faces to entire bodies. Tech giants are concerned and are taking action: Google presented 3,000 deepfake videos in the hope of enabling researchers to create strategies of fighting malicious content and identifying these a lot more easily.
Instances where in Deepfake came into picture.
- Automated attacks & targeted hacking using artificial intelligence is a major threat to look out for in 2020.
- Deepfakes, AI-manipulated videos that make it appears like someone is doing or even saying something they never really did, is at the forefront of technology.
- In 2019, high-profile edits or deepfakes have disrupted politics, mocked the most favored TV show on the globe, and inspired activity by US senators and also the Pentagon.
- The manipulations are new, just surfacing from specific Reddit users in 2017, mostly adding celebrity faces into pornographic videos.
- The rapid development from porn to popular culture has researchers scrambling to continue in an attempt to produce detection software which might stop deepfakes from being used to spread disinformation.
- Reddit waited till February 2018 to prohibit the deepfakes subreddit and upgrade the policies to broadly ban pornographic deepfakes.
- The technologies, while posing a risk on several fronts, could also be legally used for satire, art, comedy, and critique.
Impact of Deepfake on several Sectors
Cyber-criminals love deepfake because they do not need to target your systems. Everything is available on social networking platforms and emails. In a nutshell, one does not need to have ‘special’ hacking skills to implement cybersecurity attacks and this is the most dangerous threat to the community.
Since 2020 is an election year for the United States, rise in disinformation and deepflakes may lead to false campaign.
-
Deepfake impacking the economy.
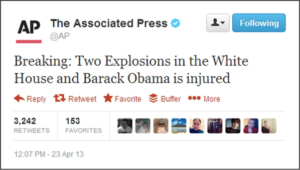
A single fake tweet regarding explosions in the White House that had injured former US president Barack Obama to wipe out more than US$130 billion available in stock value in just a few minutes.
It can be used to manipulate stock prices when altered footage of the leaders of the Tech giants making certain claims gets viral. Imagine what would be the impact, if a fake clip of the CEOs of tech giants like Apple, Microsoft, Amazon, or Google declaring they have done something illegal. For example, in 2008, Apple’s stock dropped 10 points believing in a false rumor that Steve Jobs had suffered a major heart attack that emerged.
Hackers are able to make your business financially weak without accessing your balance sheet. Spreading misinformation in the market-leading to increase and decrease in the shares of the organization, based on the intentions of the hacker.
-
Deepfake ransomware.
Attackers are able to produce extremely damaging video and audio clips. With the threat of uploading everything online, hackers are able to extort money, data, or perhaps both. It is no surprise Deepfake ransomware is among the most feared potential future cyber attack vectors.

The company thinks the kind of ransomware, which requires an attacker taking a choice of the swathe of pictures people post online and use to generate an embarrassing or scandalous video like pornography or maybe violent behaviour, may begin to spread in the near future. Due to the chance that this particular type of footage may be career-ending at least.
Deepfake ransomware may also target teenagers, the number of images they upload online and the frequency of the pictures being uploaded makes them an easy target for attackers.
-
Deepfake enabling the next “Big Data Breach”.
Up till this stage, by far the most widely circulated deepfake videos have mainly all been developed with the intention to make viewers laugh.
Say you are an IT manager, hackers are going to scrutinize your social media to gather audio and video bits. A deepfake media is going to be created to fool the subordinates into providing access to vulnerable databases. Result: Data breach with a catastrophic scale.
However, the dark web had already done enough for ID thieves, deepfake is helping these thieves to achieve what they had not done earlier. Deepfake with the assistance of social networking makes impersonating anyone easier.
-
Deepfake impacting Politics.
We already have discussed that this year will be the election year for the United States. Deepfakes may influence elections since they are able to put words directly into politicians’ mouths and make them look as they have done or even said certain things which, in fact, they haven’t. Deepfake producers might focus on popular social networking platforms, in which the content shared can immediately become viral. This could lead to false campaigns which in-return may affect the elections.
-
Online bullying.
The deepfake technology might also be applied for cyber-bullying since it is now becoming widely accessible. Users can easily turn into victims when modified media of them is uploaded online. They are blackmailed by cyber-criminals that are threatening to leak the footage if, they do not full-fill the requirements of the blackmailer.
-
Supply Chain and third party attacks.
As big firms invest heavily in cybersecurity, attackers are prone to turn the focus on much easier, less-funded and smaller targets. Third-party vendors for massive organizations. He predicted that these kinds of attacks are prone to take place in areas including health care, automobile, and broadcasting
How can you protect your Data and Business from Deepfakes
Deepfake technology is challenging. However, there are still ways to protect your data and business both.
No matter how good technological deepfake detection techniques could be, they will not avoid manipulated media from being discussed and reach a large number of users. Thus, the most effective way is teaching the employees exactly how to determine fake footage and question all that looks suspicions inside the business.
-
Train your organization
Add deepfake as an important aspect of your cybersecurity training. For example, if in case they get an unexpected call from the CEO who’s asking them to transfer $1 million to an account, they could, first of all, the question in case the person on the other line is who they claim they’re. Perhaps, a great countermeasure would be having a couple of security questions input that has to be asked to confirm a caller’s identity.
-
Monitoring online presence
Your brand’s online existence is most likely being monitored. So, ensure your designated employee keeps an eye on fake content involving the organization and if anything suspicious is noticed, they do their utmost to have it down quickly and mitigate the damage.
-
Transparency
If you are on the radar of hackers creating deepfake, guarantee that your clients are aware of the attack. Attempting to ignore what happened or even think that people did not believe what they have seen or even read will not make the matter disappear. Thus, your PR efforts must be focused around communicating that someone out of your organization has become impersonated and highlighting the artificial nature belonging to the distributed footage.
Results of Deepfake when implemented
- FakeApp
In January 2018, a desktop application was made available for free download, bringing deepfakes to the masses.
The software was initially getting peddled by a user known as deepfake app on Reddit and used Google’s TensorFlow framework.
The readily accessible technology really helped increase the dedicated deepfakes subreddit this sprung up following the first deepfakes Vice article.
People who used the software, that had been linked and defined in the subreddit, shared their own creations and comment on others. The majority of it had been reportedly pornography, but several other movies were lighter-hearted, featuring movie scenes with the actor face swapped in with Nicholas Cage’s face.
- A video of Barack Obama saying words that weren’t his own.

In April 2018, BuzzFeed published a frighteningly realistic video that went viral of a Barack Obama deepfake which it’d commissioned. Unlike the University of Washington video, Obama was created saying words that were not his own.
The video clip was produced by a single person with FakeApp, that reportedly took 56 hrs to scrape and aggregate a unit of Obama. While it was transparent with regards to simply being a deepfake, it absolutely was a warning shot for the harmful possibility of the technology.
- An edited video clip of Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez

In July 2018, an edited video went viral of an interview with Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez with 4 million views.
The video, that cuts the original interview and inserts a different host rather, makes it show up like Ocasio-Cortez struggled to answer simple questions. The video blurred the series between satire and something which may be a genuine attempt at smearing Ocasio Cortez.
As outlined by The Verge, commenters responded with claims like, “complete moron” & “dumb as a box of snakes,” which makes it not clear just how many a lot of people in fact fooled.
- A slowed down video of Democratic Speaker of the House Nancy Pelosi
In May 2019, a slowed-down clip of Democratic Speaker of the House Nancy Pelosi went viral on Twitter and Facebook. The clip was slowed down to make her appear like she was slurring her speech, as well as inspired commenters to challenge Pelosi’s psychological state.
The video, while not really a deepfake, was one of the most impacted video manipulations targeting a high government official, more than 2 million views and obviously tricking numerous commenters.
The viral threat of video manipulation was when Trump’s personal lawyer Rudy Giuliani shared the video clip, in addition to Trump tweeting out another edited video of Pelosi.
Despite the reality that the video clip was fake, Facebook publicly refused to eliminate it, rather tossing the duty to its third-party fact-checkers, who may just create info that seems alongside the video. In reaction, Pelosi poked Facebook, “they wittingly had been enablers and accomplices of false information to go across Facebook”.
The video has since disappeared off Facebook, but Facebook says it did not delete it.
5. A deepfake video of Mark Zuckerberg appeared on Instagram

Shortly after Nancy Pelosi deepfake video, a deepfake video of Mark Zuckerberg appeared on Instagram, portraying a CBSN segment that never happened, where Mark Zuckerberg was saying “Imagine one person, with complete control of billions of people’s stolen data, all the secrets, their lives, the futures. I owe everything to Spectre. Spectre demonstrated to me that anyone who controls the data controls the future.” Spectre was an art exhibition that featured several deepfakes produced by artist Bill Posters and an advertising company. Posters say the video clip was a critique of big tech.”
Conclusion
The dangers of deefakes are real and shouldn’t be underestimated. A single ill-intended rumor could eliminate your business. Thus, you, both as an organization and an individual, should be ready to stand from these threats.
Despite all we have written up to this point, there are still many good things to look out for, particularly as far as the battle against deepfakes is concerned.
First of all, as increasingly more people are beginning to educate themselves regarding the deepfake tech, and the implications the technology has on false information. At the conclusion of the article, we would love to remind our readers to look at the authenticity of each and everything they read, see or hear online. In this era of evolving technologies deepfakes can also be used as a positive aspect of artificial intelligence.