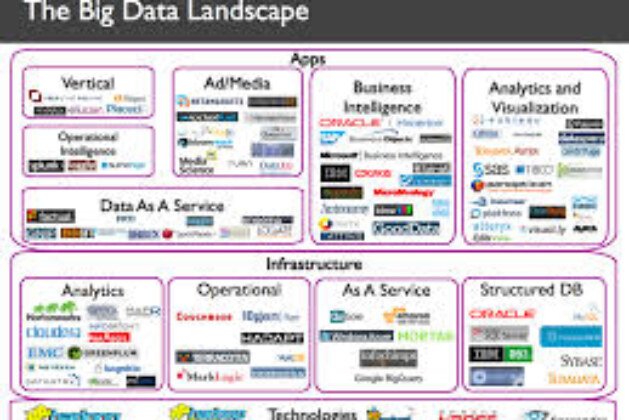
For the uninitiated, the Big Data landscape can be daunting. The great proliferation of technologies in that competitive market mean there is no individual go to option when you start building your Big Data structure. In this particular sequence of articles, we are going to examine the Big Data ecosystem, as well as the multivarious technologies that can be found to help enterprises harness the data of theirs. This very first article is designed to serve as a simple map, a short introduction of the key choices readily available for those taking the initial steps into the vastly lucrative world of Big Data as well as Analytics.
Ultimately, a big Data atmosphere ought to let you save, procedure, analyse visualise information. It starts off together with the infrastructure, and choosing the correct resources for storing, processing and sometimes analysing. There are then specialised analytics equipment that will help you locate the insights within the information. Further on as a result of this, there are applications that run off the prepared, analysed data. All of these’re important parts of the big Data environment.
INFRASTRUCTURE
Infrastructural technologies are actually the center of the Big Data environment. They process, grocery and typically also analyse data. For years, enterprises relied on relational databases typical collections of tables- and rows for processing organized data. Nevertheless, the volume, velocity as well as variety of information mean that relational databases frequently can’t provide the performance and latency needed to deal with big, complex data. The rise of unstructured details particularly meant that information capture had to move over and above simply tables and rows. Thus latest infrastructural technologies emerged, able to wrangling a great assortment of information, and making it feasible to operate applications on systems with a huge number of nodes, possibly involving a huge number of terabytes of information.
Some of the key infrastructural technologies include:
- Hadoop- An entire ecosystem of technologies created for the storing, analysing and processing of data. The core Hadoop technologies focus on the basic principle of busting up and distributing information into components and analysing those components concurrently, instead of dealing with one monolithic block of information all in a single go.
- NoSQL- Stands for Not only SQL; additionally needed in processing big volumes of multi structured data. Most NoSQL databases are very skilled at handling discrete details stored among multi structured data. Some NoSQL databases, such as HBase, will work concurrently with Hadoop.
- Massively Parallel Processing (MPP) Databases- MPP databases job by segmenting information across numerous nodes, as well as processing these segments of information in parallel, as well as employs SQL. Whereas Hadoop is normally operate on discount clusters of commodity servers, many MPP databases operate on costly specialised hardware.
Many businesses make use of combinations of the 3 (and other) types of Infrastructure technologies in their Big Data atmosphere.
ANALYTICS

Though infrastructural technologies combine data analysis, you will find particular technologies that are created especially with analytical abilities in mind. Sub-categories of analytics on the important data map include:
- Analytics Platforms- Integrate and analyse information to uncover brand new insights, as well as assistance businesses make better informed decisions. There’s a specific focus on this particular area on latency, and driving insights to end users within probably the most timely fashion possible.
- Visualization Platforms- Specifically designed as the title may suggest for visualizing information; taking the raw information and showing it in complex, multi dimensional visual formats to light up the info
- Business Intelligence (BI) Platforms- Used for integrating as well as analysing information especially for businesses. BI Platforms analyse information from several sources to provide services like business intelligence reports, visualizations and dashboards
- Machine Learning- Although is dissimilar to the others, also falls under this category. Whereas the analytics os’s feedback ready-made information and paper analytics/dashboards/visualizations for conclusion computer users, the type in contained printer learning is actually information the algorithm’ learns from’, as well as the output is dependent on the use situation. One of the more prominent examples is actually IBM’s great computer Watson, that has’ learned’ to in scanning huge quantities of info to locate certain answers, and can easily brush through 200 million web pages of organized and unstructured details in mins. The computer not too long ago combed through recipes as well as taste combinations to create its own sauce.
APPLICATIONS
Apps are actually big data companies and startups which revolve close to taking the analysed large data and making use of it to provide end users optimised insights. Fields in which apps are used include:
- Health- Mintlabs is a compendium of 3d mind resulting scans as well as neurological info which may be seen by neurosurgeons from all around the planet and guidance in the examination, prognosis, and therapy of individuals with brain diseases
- Retail- Avansera run mobile shopping apps which provide insights for food output companies directly into variables which impact food buy, like brand loyalty and cost flexibility
- Energy- AutoGrid uses information through smart meters, building management systems, thermostats and voltage regulators to assist customers track and curb power consumption, reduce waste, sense of balance the grid, enhance system operations and perhaps predict future consumption.
- Source: EILEEN MCNULTY from the data economy